Microsoft Windows shortcut keys
Shortcut Keys
|
3.x
|
95
|
98
|
ME
|
NT
|
2000
|
XP
|
Vista
| |
Alt + Tab
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Switch between open applications.
|
Alt + Shift + Tab
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Switch backwards between open applications.
|
Alt + double-click
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Display the properties of the object you double-click on. For example, doing this on a file would display its properties.
| |
Ctrl + Tab
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Switches between program groups or document windows in applications that support this feature.
|
Ctrl + Shift + Tab
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Same as above but backwards.
|
Alt + Print Screen
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Create a screen shot only for the program you are currently in.
|
Ctrl + Alt + Del
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Reboot the computer and/or bring up the Windows task manager.
|
Ctrl + Esc
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Bring up the Windows Start menu. In Windows 3.x this would bring up the Task Manager.
|
Alt + Esc
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Switch Between open applications on taskbar.
| |
F1
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Activates help for current open application.
|
F2
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Renames selected Icon.
|
F3
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Starts find from desktop.
| |
F4
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Opens the drive selection when browsing.
| |
F5
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Refresh Contents.
| |
F10
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Activates menu bar.
|
Shift + F10
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Simulates right-click on selected item.
| |
F4
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Select a different location to browse in the Windows Explorer toolbar.
| |
Alt + F4
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Closes Current open program.
|
Ctrl + F4
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Closes Window in Program.
|
F6
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Move cursor to different Windows Explorer pane.
| |
Ctrl + Space bar
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Drops down the window control menu.
|
Ctrl + (the '+' key on the keypad)
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Automatically adjust the widths of all the columns in Windows explorer
| ||
Alt + Enter
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Opens properties window of selected icon or program.
| |
Shift + Del
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Delete programs/files without throwing them into the recycle bin.
| |
Holding Shift
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Boot Safe Mode or by pass system files as the computer is booting.
|
Holding Shift
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
When putting in an audio CD, will prevent CD Player from playing.
| |
Enter
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Activates the highlighted program.
|
Alt + Down arrow
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Display all available options on drop down menu.
| |
* (on the keypad)
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Expands all folders on the currently selected folder or drive in Windows Explorer.
| |
+ (on the keypad)
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Expands only the currently selected folder in Windows Explorer.
| |
- (on the keypad)
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
X
|
Collapses the currently selected folder in Windows Explorer.
| |
Windows key keyboard shortcuts
Below is a listing of Windows keys that can be used on computers running a Microsoft Windows operating system and using a keyboard with a Windows key. In the below list of shortcuts, the Windows key is represented by "WINKEY".
| Shortcut Keys | Description |
| WINKEY | Pressing the Windows key alone will open Start. |
| WINKEY + F1 | Opens the Microsoft Windows help and support center. |
| WINKEY + F3 | Opens the Advanced find window in Microsoft Outlook. |
| WINKEY + D | Brings the desktop to the top of all other windows. |
| WINKEY + M | Minimizes all windows. |
| WINKEY + SHIFT + M | Undo the minimize done by WINKEY + M and WINKEY + D. |
| WINKEY + E | Open Microsoft Explorer. |
| WINKEY + Tab | Cycle through open programs through the taskbar. |
| WINKEY + F | Display the Windows Search / Find feature. |
| WINKEY + CTRL + F | Display the search for computers window. |
| WINKEY + F1 | Display the Microsoft Windows help. |
| WINKEY + R | Open the run window. |
| WINKEY + Pause / Break key | Open the system properties window. |
| WINKEY + U | Open Utility Manager. |
| WINKEY + L | Lock the computer (Windows XP and above only). |
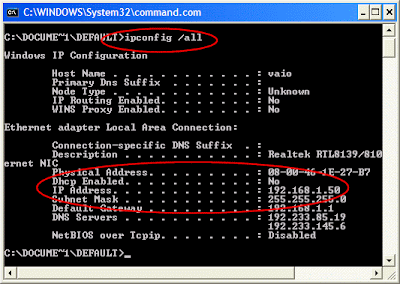
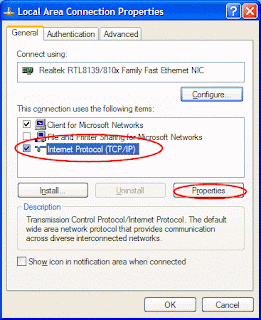 This opens the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
This opens the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.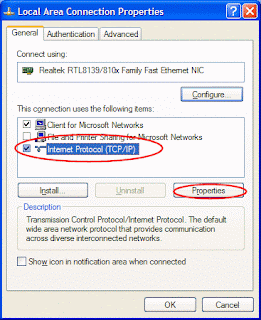 Then:
Then:

 5.This page enables you to select the hard disk drive on which Windows XP will be installed. Once you complete this step, all data on your hard disk drive will be removed and cannot be recovered. It is extremely important that you have a recent backup copy of your files before continuing. When you have a backup copy, press D, and then press L when prompted. This deletes your existing data.
5.This page enables you to select the hard disk drive on which Windows XP will be installed. Once you complete this step, all data on your hard disk drive will be removed and cannot be recovered. It is extremely important that you have a recent backup copy of your files before continuing. When you have a backup copy, press D, and then press L when prompted. This deletes your existing data.








 Part 3: Complete the installation
Part 3: Complete the installation 17. When the Monitor Settings dialog box appears, click OK.
17. When the Monitor Settings dialog box appears, click OK. 18. The final stage of setup begins. On the Welcome to Microsoft Windows page, click Next.
18. The final stage of setup begins. On the Welcome to Microsoft Windows page, click Next. 19. On the Help protect your PC page, click Help protect my PC by turning on Automatic Updates now. Then, click Next.
19. On the Help protect your PC page, click Help protect my PC by turning on Automatic Updates now. Then, click Next.
 If you use dial-up Internet access, or if Windows XP cannot connect to the Internet, you can connect to the Internet after setup is complete. On the How will this computer connect to the Internet? page, click Skip.
If you use dial-up Internet access, or if Windows XP cannot connect to the Internet, you can connect to the Internet after setup is complete. On the How will this computer connect to the Internet? page, click Skip. 21. Windows XP Setup displays the Ready to activate Windows? page. If you are connected to the Internet, click Yes, and then click Next. If you are not yet connected to the Internet, click No, click Next, and then skip to step 24. After setup is complete, Windows XP will automatically remind you to activate and register your copy of Windows XP.
21. Windows XP Setup displays the Ready to activate Windows? page. If you are connected to the Internet, click Yes, and then click Next. If you are not yet connected to the Internet, click No, click Next, and then skip to step 24. After setup is complete, Windows XP will automatically remind you to activate and register your copy of Windows XP.
 24. On the Who will use this computer? page, type the name of each person who will use the computer. You can use first names only, nicknames, or full names. Then click Next. To add users after setup is complete or to specify a password to keep your account private, read Create and customize user accounts.
24. On the Who will use this computer? page, type the name of each person who will use the computer. You can use first names only, nicknames, or full names. Then click Next. To add users after setup is complete or to specify a password to keep your account private, read Create and customize user accounts.
 Congratulations! Windows XP setup is complete. You can log on by clicking your name on the logon screen. If you’ve installed Windows XP on a new computer or new hard disk drive, you can now use the File and Settings Transfer Wizard to copy your important data to your computer or hard disk drive.
Congratulations! Windows XP setup is complete. You can log on by clicking your name on the logon screen. If you’ve installed Windows XP on a new computer or new hard disk drive, you can now use the File and Settings Transfer Wizard to copy your important data to your computer or hard disk drive.